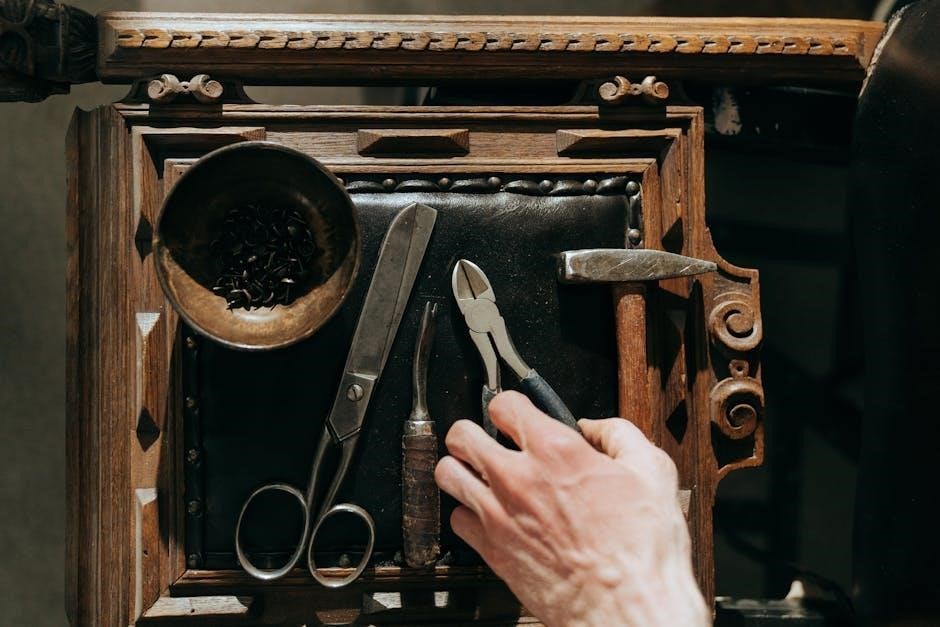
Manual Printing: An Overview
Manual printing encompasses diverse hand-printing techniques, including lithography, letterpress, and relief methods like woodcut and engraving.
Historically significant, these processes offer unique artistic expression, experiencing a modern resurgence driven by creative exploration and tactile appeal.
Access to tools empowers engineers, while technological advancements increase accessibility and user-friendliness, impacting the world of manual printing.
Historical Context of Manual Printing
Manual printing boasts a rich history, originating with ancient relief methods – notably woodblock printing in China centuries ago. This foundational technique spread across Asia, eventually reaching Europe, where it significantly impacted early book production.
The development of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg in the 15th century, while a mechanical advancement, still relied heavily on manual labor for typesetting and operation. Letterpress, a core manual technique, flourished for centuries, shaping communication and knowledge dissemination.
Lithography, emerging in the late 18th century, offered artists a new manual avenue for printmaking, distinct from relief and intaglio. Throughout the 19th and 20th centuries, various manual processes coexisted with emerging technologies, maintaining a dedicated following among artists valuing the handcrafted aesthetic and unique qualities inherent in hand-printing.
The Resurgence of Manual Printmaking
Despite the dominance of digital printing, manual printmaking is experiencing a vibrant revival in the 21st century. This resurgence is fueled by a growing appreciation for the tactile qualities and unique imperfections inherent in hand-printed works.
Artists and designers are increasingly drawn to the directness and creative control offered by techniques like letterpress, woodcut, and monoprinting. Online resources, workshops, and classes are fostering a new generation of practitioners eager to learn these traditional skills.
Furthermore, the integration of digital design tools with manual processes – using digital layouts for letterpress or scanned textures in collage – expands creative possibilities. This blend of old and new attracts artists seeking both artistic depth and contemporary expression, solidifying manual printing’s continued relevance.

Core Manual Printing Techniques
Manual printing fundamentally relies on relief, lithography, and letterpress methods, each offering distinct aesthetic qualities and requiring specialized tools for image transfer and creation.
Relief Printing: The Oldest Method
Relief printing stands as the earliest known printing technique, a process where the image to be printed is raised from a surface. This foundational method involves carving away the non-image areas, leaving the design raised to accept ink.
It can be executed using a printing press for consistent pressure or manually, utilizing tools like a barren to transfer the ink. The simplicity and directness of relief printing have made it a cornerstone of artistic expression for centuries.
This technique’s enduring appeal lies in its ability to produce bold, graphic images, and its accessibility allows for experimentation with various materials and approaches. It remains a vital practice in contemporary art.
Woodcut as a Relief Technique
Woodcut is a classic example of relief printing, traditionally employing a wooden block as the matrix. Artists carve away sections of the wood, leaving the desired image raised on the surface. This process demands careful planning, as the image is created in reverse.
Once carved, the block is inked, and then pressed onto paper – either manually using a barren or with a printing press. Woodcut is known for its bold lines and graphic quality, often resulting in striking black and white prints.
Historically significant, woodcut was widely used for book illustrations and prints before more refined techniques emerged. It continues to be valued for its distinctive aesthetic and direct, expressive nature.
Wood Engraving: Detail and Precision
Wood engraving, a refined relief printing technique, differs from woodcut through the use of the end-grain of hardwood, typically boxwood. This allows for significantly finer detail and more precise lines than can be achieved with traditional woodcut.
Artists utilize specialized tools – gravers – to carve into the wood, creating a delicate network of lines that define the image. The process is meticulous and requires considerable skill and patience. Often, wood engraving is mistaken for copperplate engraving (intaglio).
The resulting prints exhibit a remarkable level of detail and tonal variation, making wood engraving ideal for illustrations, portraits, and intricate designs. It flourished in the 19th century and remains a valued art form today.
Lithography: Printing from Stone
Lithography, meaning “stone writing,” is a manual printing technique based on the principle that oil and water repel each other. Traditionally, artists draw directly onto a smooth, flat limestone surface with a greasy crayon or tusche.
This creates an image that attracts ink, while the non-greased areas repel it. After treatment with chemicals to fix the image, the stone is dampened with water, and then inked. Paper is then pressed onto the stone, transferring the image.
Lithography allows for a wide range of tonal values and painterly effects, unlike the stark contrasts of some other hand-printing techniques. It became popular in the early 19th century and continues to be practiced by artists today.
Letterpress: The Art of Impression
Letterpress is a manual printing technique where inked, raised surfaces are pressed into paper, creating a tactile impression. Historically, this involved movable type – individual letters and characters assembled to form words and images.
Today, letterpress often utilizes photopolymer plates created from digital designs. These plates are mounted onto a press, inked with specialized inks, and then pressed firmly onto the paper using significant pressure.
The resulting prints exhibit a distinctive, debossed quality, valued for its luxurious feel and vintage aesthetic. Letterpress is celebrated for its craftsmanship and the unique character it imparts to each impression, making it a favored choice for invitations and artistic prints.

Manual Printing Processes Explained
Manual printing relies on matrix preparation, careful inking application, and consistent pressure to transfer images onto paper, yielding unique, handcrafted results.
Preparing the Printing Matrix
Preparing the printing matrix is a foundational step in manual printing, varying significantly based on the chosen technique. For relief methods like woodcut or wood engraving, this involves carving the design into a wood block, removing areas that won’t hold ink.
Lithography requires treating a stone or metal plate to create a surface that accepts ink only in the desired areas. Letterpress utilizes meticulously arranged movable type or etched metal plates.
Regardless of the method, the matrix must be carefully prepared to ensure a clean, consistent transfer of the image. This often involves cleaning, surface treatment, and, in some cases, applying protective coatings to prevent unwanted inking or damage. The quality of the matrix directly impacts the final print’s clarity and detail.
Inking the Matrix
Inking the matrix is a crucial stage in manual printing, demanding precision to achieve a quality impression. Traditionally, printing inks are applied using rollers, ensuring an even coating across the prepared surface. The type of ink selected depends on the printing technique; oil-based inks are common for lithography and letterpress, while water-based inks suit some relief methods.
The inking process requires careful control of pressure and ink quantity. Too little ink results in a faint print, while excessive ink can cause blurring or smudging. Skilled printers utilize techniques to distribute the ink uniformly, avoiding voids or build-up.
Consistent inking is paramount for repeatable results and a visually appealing final product, directly influencing the print’s tonal range and vibrancy.
Applying Pressure for Transfer
Applying pressure is the pivotal moment in manual printing where the inked image transfers from the matrix to the chosen substrate, typically paper. This is achieved through various methods, ranging from hand-rubbing for simpler techniques like woodcuts, to utilizing the substantial force of a printing press for letterpress or lithography.
Consistent and even pressure distribution is essential for a clear, well-defined print. Insufficient pressure yields a weak impression, while excessive pressure can damage both the matrix and the paper.
Manual presses allow for precise control over pressure settings, enabling printers to fine-tune the process for optimal results. The choice of paper also impacts pressure requirements; softer papers necessitate gentler application.

Tools and Materials for Manual Printing
Manual printing requires specialized tools like presses, rollers for inking, and appropriate papers; inks are applied evenly using rollers or pads for optimal results.
Printing Presses (Manual Operation)
Manual printing presses are central to many techniques, offering controlled pressure for transferring ink from the matrix to the paper. These presses range from simple tabletop models ideal for small-scale projects to larger, more robust floor-standing machines capable of handling bigger prints.
Unlike automated presses, manual operation demands physical effort – the printer manually cranks a wheel or lever to apply pressure. This direct involvement allows for greater control over the impression, enabling nuanced adjustments to achieve desired effects.
The pressure applied is crucial; too little results in a faint image, while excessive pressure can distort the paper or damage the matrix. Skilled printers develop a feel for the correct pressure through experience. Different press designs cater to specific techniques, such as letterpress or relief printing, influencing the quality and characteristics of the final print.
Rollers and Ink Distribution Tools
Rollers are indispensable in manual printing, responsible for evenly distributing ink across the printing matrix. Traditionally crafted from materials like rubber or leather, modern rollers often utilize synthetic compounds for durability and consistent performance.
The process involves carefully rolling ink across a flat surface, then transferring it to the matrix. Achieving a uniform ink film is critical; uneven distribution leads to inconsistent print quality. Different roller hardnesses are suited to various inks and matrix surfaces.
Beyond rollers, tools like palette knives and inking plates aid in managing and preparing the ink. These tools facilitate mixing, adjusting ink viscosity, and ensuring a smooth, workable consistency. Proper ink distribution is a foundational skill for successful manual printing, directly impacting the clarity and vibrancy of the final image.
Papers Suitable for Manual Printing
Selecting the right paper is crucial for successful manual printing, significantly impacting the final aesthetic and longevity of the artwork. Different techniques demand different paper characteristics. For relief printing, a sturdy, slightly textured paper is ideal, capable of withstanding the pressure of the press.
Lithography benefits from smoother, less absorbent papers to allow for detailed ink transfer. Letterpress often utilizes softer, thicker stocks to create a pronounced impression. Weight (measured in gsm or lbs) is a key consideration; heavier papers offer greater durability.
Beyond weight, fiber content, surface texture, and acidity levels influence print quality. Archival-quality, acid-free papers are recommended for artwork intended for preservation. Experimentation with various papers is encouraged to discover how different surfaces interact with inks and techniques.

Advanced Manual Printing Techniques
Advanced techniques, like monoprinting, collage combinations, and multi-block layering, expand creative possibilities within manual printing, offering unique artistic expression.
Monoprinting: Unique Impressions
Monoprinting stands as a captivating manual printing technique, celebrated for its capacity to yield utterly singular and unrepeatable impressions. Unlike methods relying on fixed matrices, monoprinting involves creating an image directly on a smooth, non-absorbent surface – often a plexiglass or metal plate.
Artists apply inks, paints, or other media to this surface, then transfer the image to paper using manual pressure. The resulting print is a one-of-a-kind artwork, as the initial image is altered or destroyed during the transfer process. This spontaneity and unpredictability are central to the technique’s appeal.
Monoprinting allows for expressive mark-making, textural exploration, and layering of colors, making it a favored method for artists seeking immediate and intuitive results. It frequently combines well with collage elements, further enhancing its unique character.
Collage and Printmaking Combinations
The fusion of collage and manual printmaking techniques unlocks a realm of exciting artistic possibilities, enriching both disciplines. Artists frequently integrate pre-existing materials – paper scraps, fabrics, found objects – directly onto the printing matrix before inking and transferring the image.
This approach introduces textural diversity and visual complexity to the final print. Alternatively, prints themselves can become elements within a larger collage composition, layered and combined with other materials to create mixed-media artworks.
Monoprinting, in particular, lends itself beautifully to collage, as its spontaneous nature complements the assemblage process. Such combinations allow for unique visual narratives, blending the reproducible qualities of printmaking with the singular character of collage.
Multi-Block Printing: Layering Colors
Multi-block printing is a sophisticated manual printing technique enabling the creation of richly colored images through successive layers. This process involves carving separate printing blocks – typically wood or linoleum – each dedicated to a single color or tonal value.
Each block is inked individually and then carefully aligned and pressed onto the paper, building up the image gradually. Precise registration is crucial to prevent color misalignment, demanding skill and patience from the printmaker;
The order in which blocks are applied significantly impacts the final result, influencing color mixing and visual depth. This method allows for nuanced color gradients and complex compositions, exceeding the limitations of single-block printing, offering artists expansive creative control.
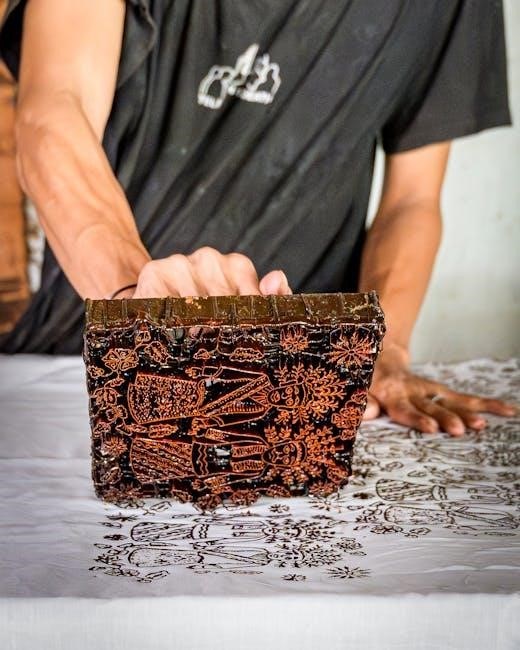

Digital Integration with Manual Printing
Digital design streamlines print matrix creation, while scanning and manipulation enhance manual prints, bridging traditional artistry with modern technology for innovative results.
Using Digital Design for Print Matrices
Digital tools revolutionize the creation of printing matrices for manual printing techniques. Artists now utilize software to design intricate patterns and imagery, offering precision previously unattainable through purely manual methods.
This digital workflow allows for easy modification and experimentation with designs before committing to the physical matrix. Complex geometric shapes, detailed illustrations, and photographic elements can be seamlessly integrated into the artwork.

Once finalized, these digital designs are then transferred onto the chosen matrix – be it a woodblock, linoleum sheet, or lithographic stone – using various methods like laser etching, inkjet printing onto transfer paper, or direct drawing based on the digital template.
The integration of digital design expands creative possibilities, enabling artists to achieve greater complexity and control in their manual printing endeavors.
Scanning and Manipulating Manual Prints
Scanning manual prints opens a realm of possibilities for digital integration and artistic manipulation. High-resolution scans capture the nuances of texture, ink distribution, and subtle imperfections inherent in hand-printed artwork.
These digital images can then be imported into image editing software, allowing artists to adjust colors, contrast, and levels, enhancing specific details or creating unique visual effects. Layers can be added, combining multiple prints or incorporating digital elements.
Furthermore, scanned prints can be digitally collaged, resized, and repeated to create larger compositions or patterns. This process bridges the gap between traditional manual techniques and contemporary digital art practices.
The ability to manipulate scanned prints digitally allows for experimentation and refinement, extending the life and versatility of each original manual print.

Resources and Further Learning
Online tutorials and guides, alongside workshops and classes, provide invaluable instruction in manual printing techniques, fostering skill development and artistic growth.
YouTube channels showcase demonstrations, while dedicated courses offer hands-on experience with various printing methods.
Online Tutorials and Guides
Numerous online resources cater to aspiring manual printers, offering a wealth of knowledge and practical demonstrations. Platforms like YouTube host channels dedicated to various printing techniques, such as relief printing, letterpress, and monoprinting. These videos often provide step-by-step instructions, showcasing the entire process from preparing the matrix to achieving a final, impressive print.
Beyond video tutorials, many websites and blogs offer detailed guides and articles covering specific techniques, materials, and troubleshooting tips. These resources often include photographic documentation and downloadable templates, aiding in the learning process. Searching for terms like “hand printing tutorial” or “relief printing guide” will yield a diverse range of options, suitable for beginners and experienced artists alike. Exploring these digital avenues provides accessible and affordable learning opportunities for anyone interested in the art of manual printing.
Workshops and Classes
Immersive learning experiences are readily available through manual printing workshops and classes offered by art centers, universities, and independent artists. These hands-on sessions provide invaluable guidance from experienced instructors, allowing participants to directly engage with the tools and techniques. Workshops often focus on specific methods, such as letterpress or wood engraving, offering in-depth exploration of the process.
Classes typically cover a broader range of printing techniques, providing a foundational understanding of the art form. The benefit of in-person instruction lies in the immediate feedback and personalized assistance, accelerating skill development. Searching online for “printmaking workshops near me” or checking local art school listings can reveal available opportunities. These experiences foster a collaborative learning environment and provide access to specialized equipment often unavailable for individual use.